Comprehensive Guide on Placenta Percreta: Know what Medical Research Reveals!

Pregnancy is a time of joy and anticipation, but it can also come with unexpected challenges. Placenta percreta is one such challenge, a rare but high-risk condition that requires careful attention. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the complexities of placenta percreta, exploring its definition, dangers to pregnant women, symptoms, causes, available treatments, and a comparison with other placental abnormalities.
What is Placenta Percreta?
Placenta percreta is a serious condition during pregnancy where the placenta grows too deeply into the uterine wall. In this rare and severe form of placental abnormality, the placenta not only attaches to the uterine wall but penetrates through it, sometimes even invading nearby organs like the bladder. This abnormal attachment can make childbirth extremely complicated and risky.
How Dangerous is Placenta Percreta for Pregnant Women?
Placenta percreta is highly dangerous for expectant mothers. The main danger lies in the risk of severe bleeding, which can occur during childbirth when doctors try to detach the placenta. This excessive bleeding can be life-threatening and often necessitates emergency medical interventions.
What are the Symptoms of Placenta Percreta?
Symptoms of placenta percreta can be subtle and may not always manifest, but they can include:
- Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding: Unusual, painless bleeding during the later stages of pregnancy or in the third trimester.
- Pelvic Pain: Persistent or intermittent pelvic discomfort or pain.
- Reduced Fetal Movements: Decreased fetal movements or changes in the baby’s activity patterns due to potential disruptions in the placental function.
- Preterm Contractions: Premature contractions leading to preterm labor in some cases.
- Palpable Mass: In rare instances, a healthcare provider may feel a firm, irregular mass during a physical examination.
It’s crucial to note that these symptoms can overlap with other pregnancy complications.
What Causes Placenta Percreta?
Placenta percreta often occurs due to previous uterine surgeries, like C-sections, which can create an environment conducive to abnormal placental attachment. Other factors include advanced maternal age, multiple pregnancies, and certain placental and uterine abnormalities.
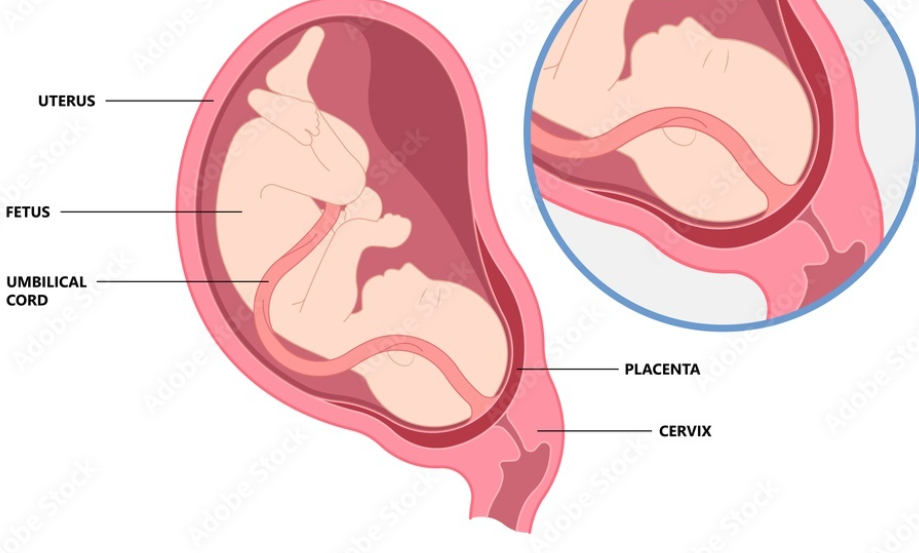
What Are the Treatments for Placenta Percreta?
The treatment for placenta percreta typically involves a multidisciplinary approach and may vary depending on the severity of the condition. Here are the main treatment options:
- Scheduled C-Section: In most cases, a planned or scheduled C-section (cesarean section) is recommended to minimize the risk of complications during childbirth. This allows healthcare providers to have a controlled environment for the delivery and immediate access to medical interventions if needed.
- Blood Transfusions: Due to the risk of severe bleeding during surgery, preparations are often made for blood transfusions to ensure an adequate blood supply is available if excessive bleeding occurs.
- Hysterectomy: In severe cases where placenta percreta is deeply invasive and uncontrollable bleeding occurs, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be necessary to save the mother’s life. This is a significant and life-altering procedure, so it’s typically considered only as a last resort.
- Advanced Surgical Techniques: Surgeons may employ various advanced techniques, such as uterine artery embolization, to control bleeding during surgery and minimize complications.
- Neonatal Care: In cases where a hysterectomy is performed, neonatal care is essential to ensure the well-being of the baby.
The specific treatment plan will depend on factors such as the gestational age of the fetus, the severity of placenta percreta, and the mother’s overall health. It’s essential that women with placenta percreta receive care from a skilled medical team experienced in managing high-risk pregnancies to maximize the chances of a safe delivery for both the mother and the baby.
Placenta Percreta vs. Other Placental Abnormalities
Placenta percreta is the most severe among placental abnormalities. It differs from placenta accreta (less severe) and placenta increta (moderate) by involving the deepest invasion into the uterine wall. This difference in severity affects the complexity of medical management and potential risks.
Conclusion
Placenta percreta is a challenging condition that demands vigilance and prompt medical attention. With early detection and advancements in medical care, there’s hope for safer pregnancies and improved outcomes for both mothers and their newborns.
FAQ’S
- Can placenta percreta be detected during routine prenatal care?
Placenta percreta is typically not detected through routine prenatal care alone. Specialized imaging techniques, such as ultrasound or MRI, are often needed for diagnosis.
2. Are there any long-term implications for women who undergo a hysterectomy due to placenta percreta?
Hysterectomy can have long-term consequences for fertility and future pregnancies. Women who have this procedure may face challenges and require careful planning if they wish to have more children.
3. Is placenta percreta preventable?
Placenta percreta is not entirely preventable, especially in cases with risk factors like prior uterine surgeries. However, early detection through prenatal care is crucial for better management and minimizing associated risks.













+ There are no comments
Add yours