“Understanding Male Fertility: 10 Proven Strategies to Enhance Sperm Count Naturally and medically”
Male fertility plays a crucial role in the journey towards parenthood. A key component of male fertility is sperm count and quality. Unfortunately, many men face challenges related to infertility, which can be a source of emotional distress and frustration. In this guide, we’ll explore male infertility, what determines sperm health, and 10 science-backed ways to boost sperm count and increase fertility naturally. We’ll also discuss foods that can help make sperm thicker and stronger, provide additional tips, and address when it might be time to seek professional help.

What is Male Infertility?
Male infertility refers to a man’s inability to impregnate a fertile female partner despite regular unprotected sexual intercourse. It is a common issue, affecting approximately 7% of men worldwide. Infertility can result from various factors, with sperm-related problems being a significant contributor.
What Determines Sperm Health?
Sperm health is a critical factor in male fertility and plays a crucial role in the process of fertilization. Several factors contribute to determining sperm health, and understanding these elements can help individuals take proactive steps to optimize their reproductive potential. Here’s a more detailed look at what determines sperm health:
- Sperm Count (Sperm Concentration):
- Sperm count, or sperm concentration, is the number of sperm cells present in one milliliter of semen. A healthy sperm count typically ranges from 15 million to 200 million sperm per milliliter. A lower sperm count can reduce the chances of fertilizing an egg.
- Sperm Motility (Sperm Movement):
- Sperm motility refers to the ability of sperm cells to move effectively and swim towards the egg. Sperm must be highly mobile to navigate the female reproductive tract and reach the egg for fertilization. Poor motility can hinder this process.
- Sperm Morphology (Sperm Shape and Structure):
- Sperm morphology evaluates the size, shape, and structure of sperm cells. Ideally, sperm should have a typical oval shape with a long tail. Abnormalities in sperm morphology can affect their ability to penetrate and fertilize an egg.
- Sperm DNA Integrity:
- The genetic quality of sperm is crucial for successful fertilization and healthy embryo development. Sperm with damaged DNA can result in infertility or increase the risk of genetic disorders in offspring.
- Semen Volume:
- Semen volume is the amount of fluid ejaculated during orgasm. While it doesn’t directly affect sperm quality, low semen volume can make it harder for sperm to reach the egg, reducing fertility.
- Hormonal Balance:
- Hormones, such as testosterone and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), play a significant role in regulating sperm production (spermatogenesis). Hormonal imbalances can disrupt this process and lead to sperm-related issues.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Lifestyle factors significantly influence sperm health. Poor habits, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and illicit drug use, can harm sperm quality. Additionally, chronic stress and exposure to environmental toxins can negatively impact fertility.
- Age:
- Advanced age can affect sperm quality. Older men may experience a decline in sperm count and motility, as well as an increase in DNA damage.
- Sexual Health:
- Conditions that affect sexual health, such as erectile dysfunction or ejaculatory disorders, can impact a man’s ability to deliver sperm effectively during intercourse.
- Underlying Health Conditions:
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity, can disrupt hormonal balance and impair sperm production.
- Medications and Treatments:
- Some medications and medical treatments, including chemotherapy and radiation therapy, can have adverse effects on sperm production and quality.
- Nutrition and Diet:
- A balanced diet that provides essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals is crucial for sperm health. Nutritional deficiencies can lead to poor sperm quality.
Understanding these factors is essential for individuals and couples seeking to optimize their fertility. If concerns arise about sperm health or fertility issues, consulting with a healthcare provider or a fertility specialist can help identify underlying causes and develop appropriate treatment plans.
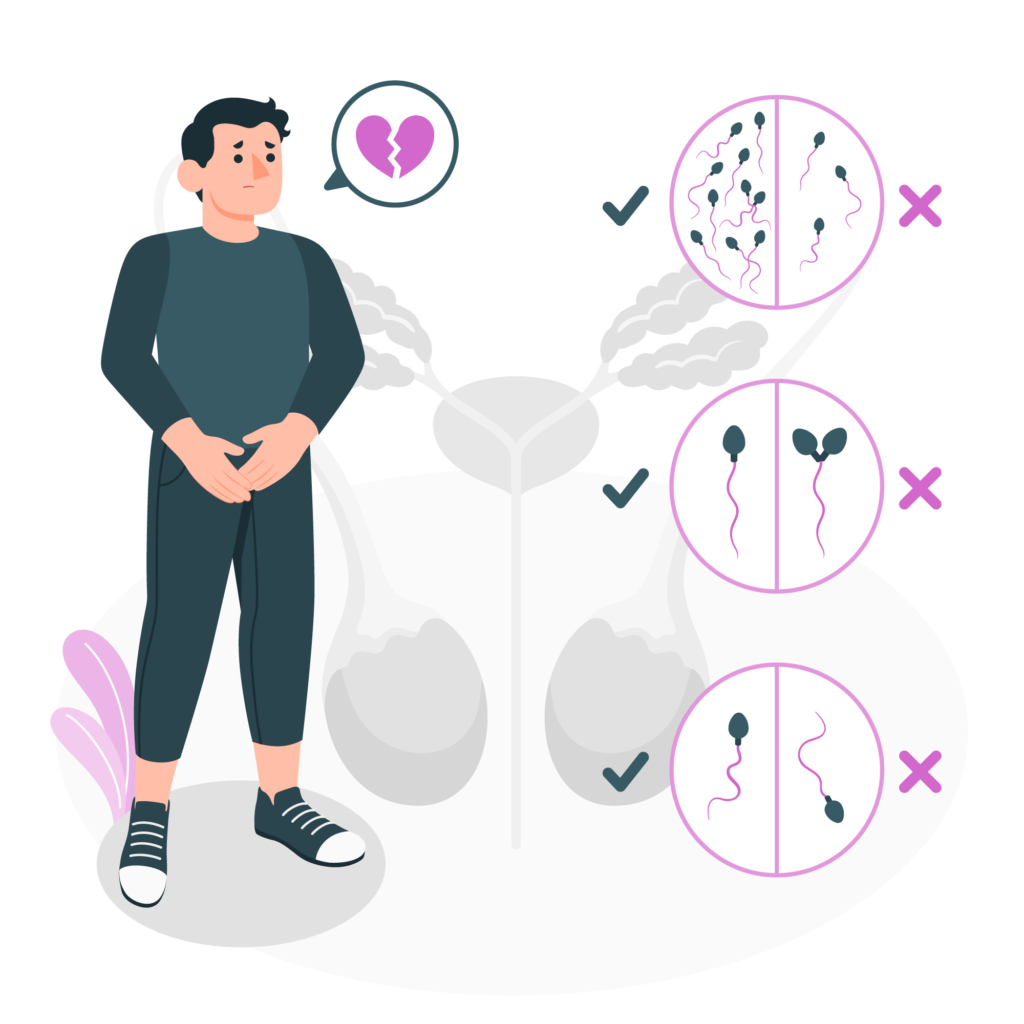
How Can I Increase My Sperm Count Naturally?
Increasing sperm count naturally involves making various lifestyle changes and adopting healthy habits. While results may take some time to become noticeable, these steps can help improve sperm count and overall sperm health. Here are some strategies:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet:
- Consume a balanced diet rich in nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your meals.
- Focus on foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, nuts, seeds, and leafy greens. Antioxidants help protect sperm from oxidative stress and damage.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Drinking enough water is essential for overall health, including sperm production. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water per day to stay properly hydrated.
- Exercise Regularly:
- Engage in moderate, regular exercise to maintain a healthy weight and support overall well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Manage Stress:
- Chronic stress can negatively impact sperm count and quality. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or mindfulness to help manage stress levels.
- Avoid Excessive Heat:
- Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can harm sperm production. Avoid hot baths, saunas, and tight-fitting underwear, as they can raise scrotal temperatures. Opt for loose-fitting, breathable underwear.
- Limit Alcohol and Tobacco:
- Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking can adversely affect sperm production and quality. Reducing or quitting these habits can improve fertility.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Obesity can disrupt hormonal balance and reduce sperm count. Aim for a healthy body mass index (BMI) by managing your weight through diet and exercise.
- Get Adequate Sleep:
- Ensure you get 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night. Proper sleep supports hormone regulation, including those related to sperm production.
- Reduce Exposure to Toxins:
- Minimize exposure to environmental toxins, such as pesticides, industrial chemicals, and pollutants. Use protective gear if you work in environments with potential hazards.
- Consider Supplements:
- Some supplements may support sperm health, but it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any. Common supplements include zinc, vitamin C, vitamin D, folic acid, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Limit Ejaculation Frequency:
- Reducing the frequency of ejaculation (e.g., abstaining from ejaculation for a few days) may allow sperm to accumulate and improve sperm count for some individuals.
- Check Medications:
- Some medications, such as certain antidepressants and steroids, can negatively impact sperm production. Discuss your medications with a healthcare provider to explore alternative options if necessary.
- Manage Chronic Health Conditions:
- If you have underlying medical conditions like diabetes or hypertension, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage them effectively, as they can affect fertility.
- Practice Safe Sex:
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can damage the reproductive system and reduce fertility. Use protection and get tested regularly if you’re sexually active with multiple partners.
Increasing sperm count naturally involves a comprehensive approach to improving overall health and well-being. Keep in mind that individual results may vary, and it’s essential to be patient as it can take several months to see significant improvements. If you have concerns about your sperm count or fertility, consider consulting a fertility specialist for personalized guidance and evaluation.
What Foods Make Sperm Thicker and Stronger?
Certain foods are believed to have the potential to improve sperm quality, making them thicker and stronger. While more research is needed to establish definitive links between specific foods and sperm health, including these items in a balanced diet can be beneficial. Here are some foods that are often associated with better sperm quality:
- Fruits and Vegetables:
- Foods rich in antioxidants, such as vitamin C and beta-carotene, can help protect sperm from oxidative stress and DNA damage. Good options include citrus fruits, strawberries, carrots, and sweet potatoes.
- Berries:
- Berries like blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are high in antioxidants, which can potentially improve sperm quality and protect against DNA damage.
- Nuts and Seeds:
- Nuts and seeds, particularly walnuts, almonds, and flaxseeds, are excellent sources of healthy fats, antioxidants, and zinc, all of which may contribute to healthier sperm.
- Leafy Greens:
- Spinach, kale, and other leafy greens are packed with folate, which is essential for sperm production and quality.
- Fish:
- Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s may enhance sperm motility and reduce inflammation.
- Oysters:
- Oysters are a well-known source of zinc, a mineral crucial for sperm production and testosterone levels.
- Eggs:
- Eggs are high in vitamin D, which has been linked to improved sperm motility and overall sperm health.
- Pumpkin Seeds:
- Pumpkin seeds are an excellent source of zinc and omega-3 fatty acids, both of which may positively impact sperm quality.
- Tomatoes:
- Tomatoes contain lycopene, an antioxidant that may help improve sperm motility and reduce the risk of DNA damage.
- Garlic:
- Garlic is known for its potential to improve blood circulation, which could benefit sperm quality. It also contains selenium, a mineral important for sperm motility.
- Dark Chocolate:
- Dark chocolate contains antioxidants, specifically flavonoids, which may have a positive impact on sperm quality when consumed in moderation.
- Pomegranates:
- Pomegranates are rich in antioxidants and have been associated with improved sperm concentration and motility.
- Avocado:
- Avocado is a source of healthy fats and vitamin E, which may support sperm health and motility.
Remember that while these foods can be part of a sperm-friendly diet, it’s essential to maintain an overall balanced and nutritious diet. No single food will miraculously transform sperm quality on its own. A combination of a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding harmful habits (like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption) is key to improving overall sperm health and fertility. If you have concerns about fertility or sperm quality, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and evaluation.
What are the Medical treatments for male infertility?
Treatment options for male infertility in the medical field vary depending on the underlying cause of infertility. It’s essential to undergo a thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider or a fertility specialist to determine the specific cause and recommend the most suitable treatment. Here are some common treatment options:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly improve sperm health. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, moderating alcohol consumption, and managing stress through relaxation techniques.
- Medications:
- Hormone therapy: Medications like clomiphene citrate or gonadotropins may be prescribed to address hormonal imbalances that affect sperm production.
- Antibiotics: If an infection is the cause of infertility, antibiotics can treat the infection and restore fertility.
- Surgical Interventions:
- Varicocele repair: Surgical correction of varicoceles (enlarged veins in the scrotum) can improve sperm production and quality.
- Vasectomy reversal: For men who have previously undergone a vasectomy but wish to restore fertility, vasectomy reversal surgery (vasovasostomy or vasoepididymostomy) may be an option.
- Sperm retrieval: Procedures like testicular sperm extraction (TESE) or percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration (PESA) can retrieve sperm directly from the testes or epididymis for use in assisted reproductive techniques.
- Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ART):
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Sperm are collected, processed, and then injected directly into the woman’s uterus during ovulation.
- In vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF involves fertilizing an egg with sperm in a laboratory dish and transferring the resulting embryo(s) into the woman’s uterus.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): In cases of severe male infertility, ICSI can be used in conjunction with IVF to directly inject a single sperm into an egg.
- Donor Sperm: In cases where there is a severe sperm-related issue that cannot be treated, couples may consider using donor sperm for insemination or IVF.
- Genetic Counseling: For couples with known genetic abnormalities that may affect fertility, genetic counseling can help assess the risk to potential offspring and explore options like preimplantation genetic testing.
- Experimental Treatments: In some cases, men with severe male factor infertility may be candidates for experimental treatments or clinical trials. These treatments are typically offered in specialized fertility centers and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
The choice of treatment depends on the specific diagnosis and individual circumstances. It’s important for couples to work closely with a healthcare provider or fertility specialist to determine the most appropriate course of action to address male infertility and increase their chances of achieving pregnancy.
Other Tips
- Reduce excessive ejaculation to allow sperm to accumulate.
- Check medications with your healthcare provider, as some may affect sperm production.
- Manage underlying health conditions like diabetes or hypertension, which can impact fertility.
When is it Time to Seek Help?
If you’ve been trying to conceive for over a year without success, it’s advisable to consult a fertility specialist. Seeking professional help early can help identify and address any underlying issues. If you want to know about the most commonly asked questions by the patient then click here: https://thebreastfeed.com/commonly-asked-questions-about-male-fertility/
Conclusion
Improving male fertility and increasing sperm count naturally involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, and making thoughtful choices. By following these science-backed recommendations and being patient, you can increase your chances of achieving the dream of parenthood. Remember that every individual is unique, so it’s crucial to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance and support on your fertility journey.
Frequently asked question
- What are the common causes of male infertility?
Common causes of male infertility include low sperm count, poor sperm motility, and abnormal sperm morphology. Other factors can include hormonal imbalances, genetic conditions, lifestyle choices (such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption), exposure to environmental toxins, and certain medical conditions like varicocele.
2. How is male infertility diagnosed?
Male infertility is typically diagnosed through a comprehensive evaluation that includes a medical history, physical examination, semen analysis, and sometimes hormonal blood tests or imaging studies. Additional specialized tests may be conducted based on the initial findings to identify specific causes.
3. What treatment options are available for male infertility?
Treatment options for male infertility depend on the underlying cause. Common treatments include lifestyle modifications, medications to address hormonal imbalances, surgical procedures to correct anatomical issues (e.g., varicocele repair), and assisted reproductive techniques like intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). The choice of treatment is individualized based on the specific diagnosis and the couple’s preferences.












+ There are no comments
Add yours