Nurturing Mother-Baby Bond: 10 Benefits of Breastfeeding for Your Little One!

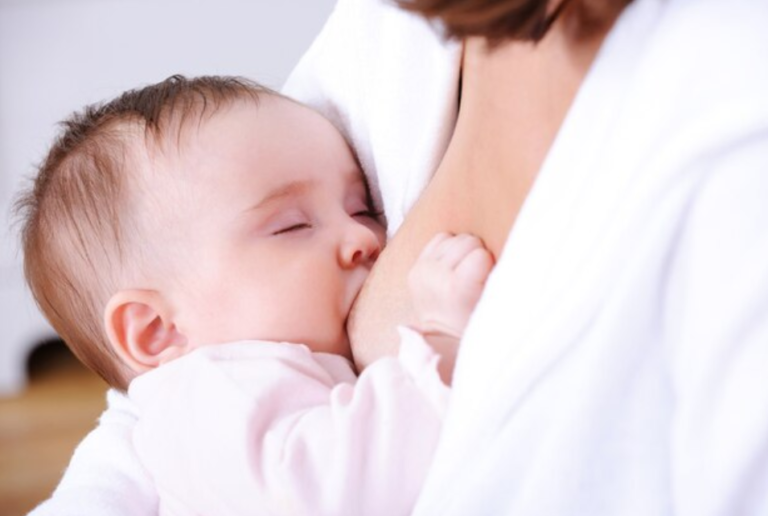
Breastfeeding is a natural and essential process that provides infants with vital nutrients and immunological protection, promoting healthy growth and development. This age-old practice is considered the gold standard for infant nutrition, offering numerous benefits for both the baby and the mother.
In this blog post, we will delve into the definition of breastfeeding, the different types and stages involved, and explore 10 Benefits of Breastfeeding for the child and the mother.
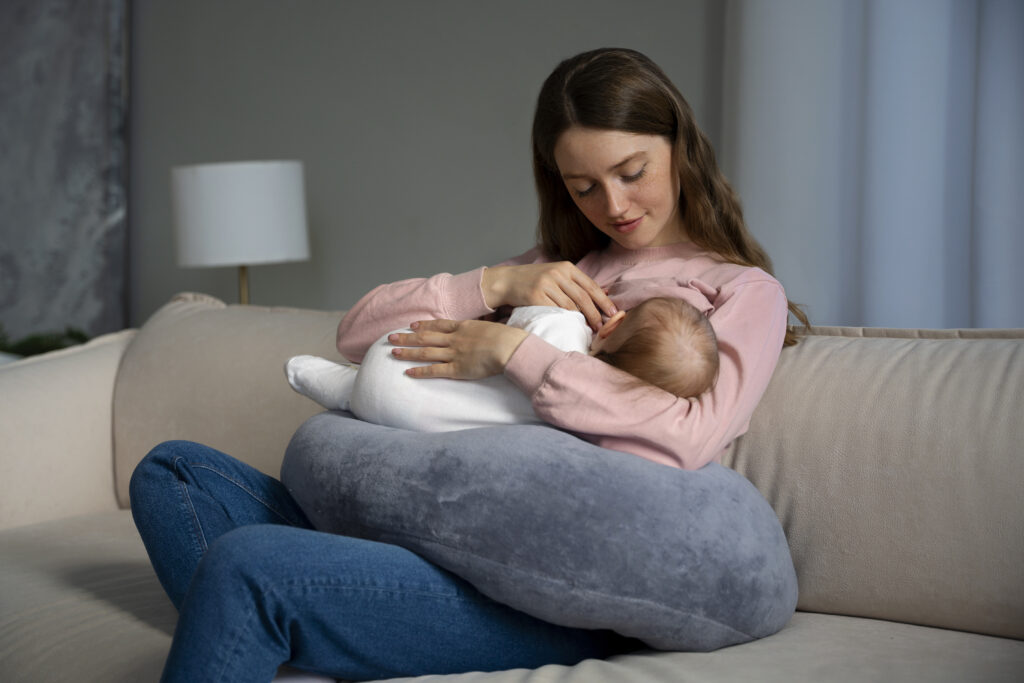

Fig: 10 Benefits of Breastfeeding for Your Little One
Definition of breastfeeding according to UNICEF
Breastfeeding, as defined by UNICEF, is the act of feeding a baby with breast milk from the mother’s breast as the primary source of nutrition. This natural process ensures that infants receive the ideal mix of nutrients tailored to their specific needs, promoting optimal growth and development.
However, the child and mother may face a few issues, but they can be managed and treated with the help of a healthcare professional. We request our readers that if they are facing any such issue, please contact the doctor.
Type of breastfeeding
There are different approaches that mothers may choose based on their unique circumstances. The two primary types are exclusive breastfeeding and partial breastfeeding.We will deal with them in points:
- Exclusive Breastfeeding: An infant is fed only breast milk without any additional formula, water, or solid foods. This is recommended for the first six months of the baby’s life, as breast milk contains all the essential nutrients the baby requires during this critical period.
2. Partial Breastfeeding: It involves supplementing breast milk with other fluids or formula. This may be necessary in specific situations where exclusive breastfeeding is not possible.
What are the stages of breastfeeding?
Before we explore the numerous benefits of breastfeeding for both the baby and the mother, it’s essential to understand the journey of breastfeeding and its different stages. From the miraculous early days of providing colostrum to the establishment of mature milk production, each stage offers unique qualities that support the baby’s growth and development.

Let’s delve into the stages of breastfeeding and uncover the incredible nourishment and bonding that it provides for both the newborn and the mother.
- Colostrum: The first few days after birth, the mother produces colostrum, a concentrated and nutrient-rich form of breast milk. It is packed with essential antibodies, protecting the newborn from infections and diseases.
- Transitional Milk: After colostrum, the milk changes to transitional milk, which is slightly more abundant and contains a balance of nutrients tailored to the baby’s needs.
- Mature Milk: Within a few weeks, mature milk is produced. This milk is thinner than colostrum but is packed with essential nutrients, promoting the baby’s overall health.
10 Benefits of Breastfeeding for the Baby
From the moment of birth, breastfeeding serves as an essential cornerstone of a baby’s well-being and development. The natural antibodies and immunological protection it provides lay the foundation for a robust immune system, protecting the little one from various infections and diseases.
Moreover, breastfeeding is not just about physical nourishment; it fosters an emotional connection between the mother and her baby, creating a sense of security and comfort. 10 benefits of breastfeeding a child are listed down below:
- Optimal Nutrition: Breast milk contains the perfect balance of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, and vitamins essential for the baby’s healthy growth and development.
- Immune System Boost: Breast milk is rich in antibodies, protecting the baby from infections, allergies, and illnesses, and providing a strong foundation for its immune system.
- Cognitive Development: Studies have shown that breastfed babies may have improved cognitive development and higher IQ levels compared to formula-fed infants.
- Digestive Health: Breast milk is easily digestible, reducing the likelihood of constipation, diarrhea, and other gastrointestinal issues in infants.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: Breastfeeding is linked to a lower risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, asthma, and certain childhood cancers.
- Bonding and Emotional Development: Close physical contact during breastfeeding fosters a strong emotional bond between the mother and the baby.
- Reduced SIDS Risk: Breastfeeding has been associated with a reduced risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
- Proper Jaw and Teeth Development: The natural sucking action during breastfeeding aids in the proper development of the baby’s jaw and teeth alignment.
- Cost-Effective: Breast milk is readily available and free, saving families from the financial burden of purchasing formula.
- Environmental Sustainability: Breastfeeding reduces the need for formula production, leading to a smaller carbon footprint and a more sustainable environment.

Breastfeeding Benefits for the Mother
Breastfeeding not only benefits the baby but also provides numerous advantages for the mother’s health and well-being. Firstly, breastfeeding promotes postpartum weight loss, as it helps the mother burn extra calories while nourishing the baby.
Additionally, breastfeeding triggers uterine contractions, aiding in the uterus’s return to its pre-pregnancy size and reducing postpartum bleeding. Studies suggest that breastfeeding may decrease the mother’s risk of breast and ovarian cancer. The benefits of breastfeeding for the mother are listed down below:
- Postpartum Weight Loss: Breastfeeding helps the mother burn extra calories, aiding in postpartum weight loss.
- Uterine Contraction: Breastfeeding triggers uterine contractions, assisting in the uterus’s return to its pre-pregnancy size.
- Reduced Risk of Breast and Ovarian Cancer: Studies suggest that breastfeeding may decrease the mother’s risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
- Emotional Well-being: The release of oxytocin during breastfeeding promotes feelings of relaxation and emotional well-being in the mother.
- Convenient and On-Demand: Breast milk is always available and at the right temperature, making feeding convenient for the mother.

Furthermore, the act of breastfeeding releases oxytocin, a hormone that fosters feelings of relaxation and emotional well-being in the mother, promoting a positive maternal bond with the baby. Moreover, breastfeeding is convenient and on-demand, as breast milk is always available and at the right temperature, saving time and effort for the mother. Emotionally and physically rewarding, breastfeeding offers a unique and intimate connection between the mother and her child.
Conclusion
Breastfeeding is a beautiful and natural process that offers a myriad of benefits for both the baby and the mother. From providing optimal nutrition and immune protection to fostering a strong emotional bond, breastfeeding plays a vital role in shaping a child’s health and development. At the same time, breastfeeding is a transformative experience for the mother. It empowers her as a provider of life, aids in postpartum recovery, and reduces the risk of certain cancers. The emotional connection she forms with her baby through breastfeeding is an irreplaceable gift that lasts a lifetime.
References
- Kalarikkal SM, Pfleghaar JL. Breastfeeding. [Updated 2023 Apr 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534767/
- Krol KM, Grossmann T. Psychological effects of breastfeeding on children and mothers. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2018 Aug;61(8):977-985. doi: 10.1007/s00103-018-2769-0. PMID: 29934681; PMCID: PMC6096620.
- Moore ML. Current research continues to support breastfeeding benefits. J Perinat Educ. 2001 Summer;10(3):38-41. doi: 10.1624/105812401X88327. PMID: 17273265; PMCID: PMC1595080.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How long should I breastfeed my baby?
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months, followed by continued breastfeeding along with appropriate complementary foods for up to two years or beyond.
2. Can I breastfeed if I have a low milk supply?
Yes, there are various techniques to increase milk supply, such as frequent breastfeeding, proper latching, and seeking support from a lactation consultant.
3. Are there any foods to avoid while breastfeeding?
Generally, breastfeeding mothers can enjoy a varied diet. However, some babies may be sensitive to certain foods. Pay attention to your baby’s reaction, and if you suspect any issues, consult a healthcare professional.
4. Can I breastfeed if I have certain medical conditions or take medications?
In most cases, breastfeeding is safe even with medical conditions or some medications. Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure it is safe for you and your baby.
5. How can I bond with my baby if I cannot breastfeed?
Bonding can happen through skin-to-skin contact, cuddling, and spending quality time with your baby. Feeding pumped breast milk or formula with a bottle can also create a strong bond between you and your little one.
Important note to readers: This blog aims to offer general awareness and promote the beauty of breastfeeding, but it is no substitute for professional medical advice. Your health and that of your baby are our utmost priority, so please rely on expert consultation to address any specific needs or concerns.













[…] Eating solids but refusing liquids: If your baby is willing to eat solids but resists liquids, this can be a strong indicator of a specific aversion to bottle or breast feeding. […]