Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS): Symptoms and Prevention Strategies
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) is a tragic and unexplained phenomenon where seemingly healthy infants die suddenly and unexpectedly during sleep. This article will delve into the definition of SIDS, its statistics, warning signs, prevention measures, etc. We’ll also address whether SIDS occurs in India and provide answers to three frequently asked questions about this devastating occurrence.

What is Sudden infant death syndrome?
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) is a tragic and unexplained phenomenon characterized by the sudden, unexpected death of an otherwise healthy infant. It generally affects the infant under one year of age, typically occurring during sleep. SIDS is sometimes referred to as “cot death” or “crib death.”
The exact cause of SIDS remains unknown; it is typically diagnosed after a thorough investigation rules out other identifiable causes of death. It is a devastating occurrence that continues to be the subject of extensive research.
Sudden infant death syndrome Statistics
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) statistics provide important insights into the prevalence and impact of this tragic phenomenon. It’s important to note that SIDS statistics may vary by region and over time. About 2,300 babies in the United States die of SIDS each year. Some babies are more at risk than others.
It’s essential to recognize that SIDS remains a significant public health concern. Local and national health authorities often track SIDS statistics to monitor trends and develop strategies for prevention.

What are the warning signs of SIDS?
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) is often sudden and unexplained, and it typically occurs during sleep, making it challenging to predict. However, there are no specific warning signs of SIDS that can be reliably identified ahead of time. While there are no definitive warning signs of SIDS, it’s important for parents and caregivers to be aware of the following risk factors:
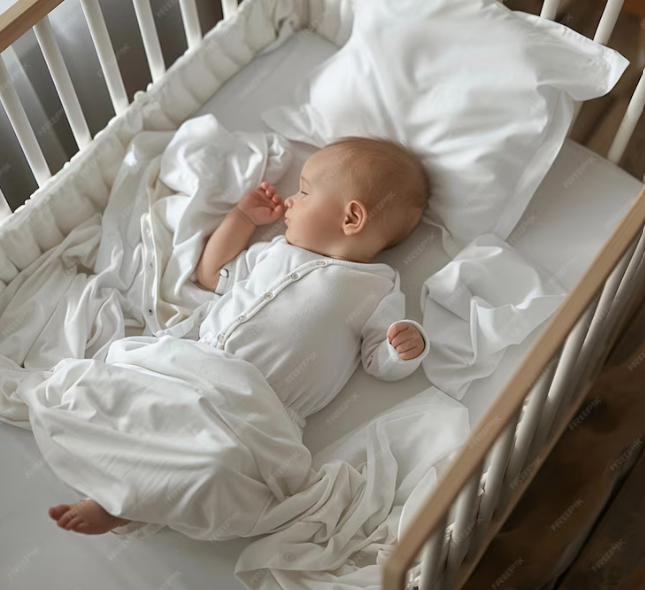
- Sleep Position: Babies should always be placed on their backs to sleep, both for naps and at nighttime. This is one of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of SIDS.
- Sleep Environment: Ensure that the baby’s sleep environment is safe.
- Sleep Location: Babies should sleep in the same room as their parents, but not in the same bed (co-sleeping), as this can increase the risk of SIDS.
- Avoid Overheating: Dress the baby in light, breathable clothing to prevent overheating during sleep.
- No Smoking: Ensure a smoke-free environment for the baby
- Pacifier Use: Consider offering a pacifier at naptime and bedtime, as it has been associated with a reduced risk of SIDS.
- Breastfeeding:Breastfeeding is linked to a lower risk of SIDS.
- Regular Prenatal Care: Receiving regular prenatal care and attending all recommended prenatal appointments can help ensure the baby’s health and reduce the risk of complications.
- Avoid Soft Bedding
- Supervised Tummy Time: While babies should sleep on their backs, supervised tummy time when the baby is awake and alert can help promote healthy development.
What are How can I prevent SIDS while sleeping?
Preventing Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) during sleep is a top priority for parents and caregivers. While there is no guaranteed method to prevent SIDS entirely, following safe sleep guidelines can significantly reduce the risk. Here are steps you can take to prevent SIDS while your baby is sleeping:
- Back to Sleep: Always place your baby on their back to sleep for all naps and at nighttime. This is the most crucial step in SIDS prevention.
- Use a Firm Sleep Surface: Ensure that your baby sleeps on a firm and flat mattress or sleep surface, such as a crib or bassinet. Avoid soft surfaces like couches, armchairs, or adult beds.
- Remove Soft Bedding: Keep the sleep environment free from pillows, quilts, comforters, stuffed animals, bumper pads, and other soft bedding materials. These can pose suffocation risks.
- Dress Appropriately: Dress your baby in light, breathable clothing appropriate for the room temperature.
- Share a Room, Not a Bed: Room-sharing is recommended for the baby’s first six months to a year. Avoid bed-sharing (co-sleeping) as it can increase the risk of SIDS.
- Use a Pacifier: Offer a pacifier for naps and bedtime. Pacifier use has been associated with a reduced risk of SIDS, although it should not be forced.
- Breastfeed If Possible: If you can breastfeed, consider doing so, as breastfeeding is linked to a lower risk of SIDS. Breast milk provides protective factors.
- Avoid Smoke Exposure: Keep the baby’s environment smoke-free, both during pregnancy and after birth. Maternal smoking during pregnancy and exposure to secondhand smoke are significant risk factors for SIDS.
- Provide Tummy Time: While the baby should always sleep on their back, supervised tummy time when the baby is awake and alert helps with motor development and strengthens neck muscles.
- Regular Prenatal Care: Receiving regular prenatal care and attending all recommended prenatal appointments can help ensure the baby’s health and reduce the risk of complications.
- Immunizations: Ensure that your baby receives recommended vaccinations on schedule. Immunizations can help protect against certain infections that may contribute to SIDS.
- Avoid Overbundling: Do not overdress your baby for sleep. Keep the room at a comfortable temperature, and use lightweight, breathable blankets if needed.
- Educate Caregivers: Share SIDS prevention guidelines with anyone who cares for your baby, such as grandparents, babysitters, and daycare providers.
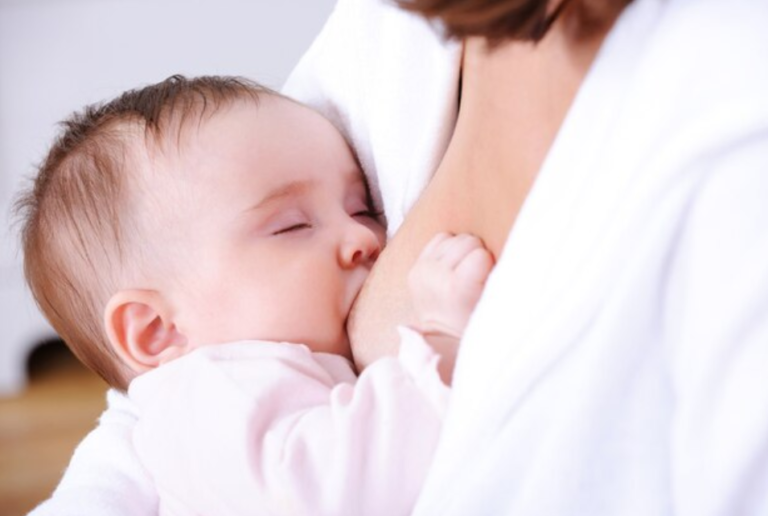
Does breastfeeding reduce SIDS?

Yes, breastfeeding has been associated with a reduced risk of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS). Breast milk provides numerous benefits to an infant’s health, including a potential protective effect against SIDS. Several factors contribute to this association:
- Immune System Boost: Breast milk contains antibodies and immunoglobulins that help bolster a baby’s immune system. This can help protect the infant against infections and illnesses, reducing the likelihood of SIDS, which is sometimes linked to respiratory infections.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Breast milk has anti-inflammatory properties that may reduce inflammation in a baby’s airways, potentially lowering the risk of breathing difficulties during sleep.
- Neurodevelopment: Some studies suggest that breastfeeding may have a positive impact on brain development, potentially reducing the vulnerability of the baby’s central nervous system to SIDS.
- Maternal Antibodies: Breastfeeding transfers maternal antibodies to the baby, enhancing their immune response to infections.
While breastfeeding is associated with a decreased risk of SIDS, it’s essential to remember that SIDS can still occur in breastfed infants. Therefore, adhering to safe sleep practices, such as placing the baby on their back to sleep and creating a safe sleep environment, remains crucial in reducing the overall risk of SIDS.
Does sleeping with baby reduce SIDS?
Sleeping with a baby, also known as bed-sharing or co-sleeping, is a controversial topic in relation to Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS). While some proponents argue that it can promote bonding and breastfeeding, the evidence on whether bed-sharing reduces the risk of SIDS is mixed, and it comes with potential risks.
Here’s what you should consider:
Pros of Bed-Sharing:
- Facilitates Breastfeeding
- Enhances Bonding
Cons of Bed-Sharing:
- Increased SIDS Risk
- Suffocation Hazards
- Tobacco or Alcohol Use
- Sleep Surfaces
Does SIDS happen in India?
While Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) is recognized as a global concern, including in India, it’s important to note that specific research and statistics on SIDS in India may be limited compared to some Western countries.
SIDS prevalence rates in India may vary across regions, making it difficult to provide a single national statistic. India has a large population, and SIDS cases may not be consistently reported or studied in all areas.
SIDS is recognized as a concern in India, comprehensive research and accurate statistics on SIDS in the country may face challenges related to data collection and regional variations. Efforts to promote safe sleep practices and gather more data on SIDS cases are essential to understanding and preventing this tragic phenomenon in the Indian context.
Conlcusion
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome is a heartbreaking and mysterious occurrence that underscores the importance of safe sleep practices and awareness. By understanding the risk factors, prevention strategies, and potential benefits of breastfeeding, we can work towards reducing the incidence of SIDS and ensuring the safety of our infants.
Frequenlty asked question
- What causes Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)?
The exact cause of SIDS remains unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of factors, including an underlying vulnerability in the baby, sleep environment risks, and critical developmental stages.
2. Can SIDS be prevented entirely?
While SIDS cannot be completely eliminated, the risk can be significantly reduced by following safe sleep guidelines, such as placing the baby on their back to sleep, using a firm mattress, and avoiding smoking near the infant.
3. Is SIDS the same as suffocation or accidental infant deaths during sleep?
No, SIDS is different from suffocation or accidental sleep-related deaths. SIDS is unexplained and occurs in seemingly healthy infants, while suffocation or accidental deaths result from known factors like unsafe sleep environments or physical obstruction.













+ There are no comments
Add yours